Explanations

In the following you will find brief descriptions of some essential Internet terms.
|
Back to: Get familiar with the basics of the Internet Back to: Potential dangers on the Internet |
♦ World Wide Web (WWW)
The World Wide Web, commonly known as the Web, is a subset of the Internet. The Web consists of pages that can be accessed by entering the website name in form of a Uniform Resource Locator (URL) in the Web browser.
The URL contains the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) which enables the access over the Internet.
The Internet is then the actual network of networks where all the information resides.
♦ Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) 
HTTP is the protocol used to transfer data over the Internet. It is part of the Internet protocol set. The HTTP provides functions utilized for transmitting webpage data in an unsecured manner.
Therefore, HTTPS (Secured) should be used when ever personal or sensitive data is entered on a website, like for online banking. It is the same as HTTP, but uses a secure socket layer (SSL) for security purposes.
♦ Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
This term is often used when entering the address for a web page in the browser. Usually, the URL is displayed in the browsers address bar.
A typical URL consists of separate parts. For example it could have the form http://www.example.com/index.html, which indicates a protocol (http or https), a host name (www.example.com) and a file name (index.html).
♦ Cookies (HTTP-, web-, Internet-, browser cookies) (Not this kind of cookie)
(Not this kind of cookie)
Here, a cookie is a small piece of data sent from a website and stored in a file on the user's device by the web browser.
Cookies were developed for websites to remember information received from the user. This can be data you entered on the website like your name, address, telephone number and so on.
But then, further information about you is possible to store there as well.
♦ Link (Hyperlink) 
A hyperlink, or simply a link, is a reference to data that the reader can directly follow by clicking or tapping.
A link points to a whole document or to a specific element within a document. Same applies for websites. Clicking a link will directly lead to the defined document or website.
The displayed text in a link can be different from the given document or website where it will lead to. It makes the document easier to read.
On the other hand, it is a risk that the link leads to a fake website that may contain harmful software. By moving the cursor on the link, you can check where the link points to.
♦ Domain Name Service (DNS) 
It is a service that translates easier to remember website names to numerical IP addresses needed for identifying computer services. On the internet, DNS automatically converts the names typed in a web browser to the IP addresses of web servers hosting those sites. This is necessary because, websites are accessed based on IP addresses.
In principle this works like a telephone book.
♦ User tracking 
Is a practice where, operators of websites collect information about you and your activities on the visited site, like:
-
your IP address
-
Internet Service Provider name
-
browser and operating system type
-
time that you spent on the website
-
what you have looked at and where you have clicked
♦ Potentially Unwanted Program or Application (PUP/PUA)
When installing free software, sometimes unwanted programs are added at the same time. In some cases, without your notice.
An unwanted program might modify the behaviour of other programs, or it is an additional security risk.
This is one good reason to follow cautiously the installation process carefully.
♦ Doxing ![]()
Doxing is a method of collecting all available information about an individual using any sources on the internet.
The name comes from “Documents” or “Docx”.
Doxing is based purely on the skills of the hacker to gather valuable information about his target and use this information to his benefit.
♦ In-App Purchases ![]()
In-app purchasing describes a method for buying goods and services from inside an application on mobile devices. Users make an in-app purchase to:
-
expand the functionality of a program
-
to access special content
-
get extra features in an app such as power-ups
-
pass to restricted levels
-
get virtual money
-
or other boosts
Very often this method is used in online-games.
There are various types of payments for the ordered items. An annoying type is automatically extended until you terminate the purchase.
♦ Social engineering 
In the context of information security, it is the psychological manipulation of people so that they release confidential information. A number of tactics may be used, including: taking advantage of human kindness.
♦ Phishing 
Phishing is the attempt to capture sensitive information like user names, passwords, credit card numbers and online banking access codes.
It is used often for criminal activities, by pretending to be a trustworthy source in an electronic communication.There are specific ways used for getting sensitive information.
A typical method is you receive an email from a well-known sender. For an urgent reason you should provide sensitive information on their website. For this a link is provided in the email. After clicking the link, a website opens that look like one from a well-known sender. In reality the site belongs to someone else, usually a hacker that will use the given information for criminal purposes.
♦ QR Code Scam (Qrshing) 
Qrshing is a form of phishing. It uses Quick Response or “QR” codes to direct users to a fake website that distributes malware or asks for confidential information.
There are several possible ways to utilize QR codes for scamming.
♦ Scamming 
Scamming is used to describe any fraudulent business or scheme that takes money or other goods from a person. For example, one scheme is a relationship of trust is build over the Internet. Finally, it leads to a fraudulent act or operation.
♦ Child grooming (Cyber grooming)
The purpose of child grooming is to establish a trustful relationship with a child. Over the Internet abusers will pretend as children and make arrangements to meet with them in person. An alarm signal is when the child should change the platform to a one with secure communication. Very often the objective is sexual abuse of a child. A more general name is cyber grooming.
♦ Drive-by Downloads (Nothing to do with Drive In) 
Drive-by downloads are malicious software downloaded to a computer, tablet or smartphone when the user views a compromised Web page.
The malware is then automatically installed without any notice, as it is done in silent mode.
♦ Ransomware (blackmail software) 
This type of malware prevents the accessing of a system or the own files by:
- Locking the systems’ screen
-
encrypting the users’ own files
Users are forced to pay a ransom for getting back the access to the system or own files.
 Paying the ransom does not guarantee that users will get back access to the locked system or encrypted files.
Paying the ransom does not guarantee that users will get back access to the locked system or encrypted files.
♦ Geo-blocking or geoblocking 
It is a technology that restricts access to content on the Internet based upon the user's geographical location. To determine the user's location very often his IP address is checked. There are various reasons for geo-blocking, such as films and television shows, primarily for copyright and licensing reasons.
♦ Virtual Private Network (VPN) 
A VPN is a private network that uses a public network (usually the Internet) to connect to remote sites.
To secure the communication inside a VPN, the traffic is encrypted. Depending on the location and speed of the server, loading of websites may take a little longer.
A VPN might enable you to get access to web content that is in your country not available, because it pretends you are located in another country.
♦ Fake news, fake shops, and fake profiles 
On the Internet everything is virtual and may not necessary exist in reality.
An online shop may have nice pictures or videos and good descriptions, but not a single item in the warehouse. Quite often they have very low prices compared to other online shops. After you have ordered something, you will not receive the item you paid for, or nothing at all.
Fake news has recently increased. It is relatively easy to spread messages on the Internet whose content is not true. Very often fake news spreads on social media.
Fake user profiles are used to hide the real identify to others on the Internet. This is very often used on social media related services. There are several reasons to hide the real identity on the web – good and bad.
♦ Deep fake 
A deep fake (deepfake) is a digitally forged image or video of a person that makes them appear to be someone else. It is the next level of intentionally producing fake content that takes advantage of artificial intelligence (AI).
This technology can be utilized for amusing videos but also for the distribution of fake content with negative impact. Deep fake technology is evolving to a point where it will be most likely problematic to distinguish fake videos from authentic ones.
♦ Bots, chat bots, or social bots 
Bots (Internet bots or web robots) are applications that perform certain tasks automated and very fast. Typically, bots perform tasks that are both simple and structurally repetitive, at a much higher speed than would be possible for a human.
Chat bots or social bots are used to communicate via auditory or textual methods with other users on Internet-based services. Such applications are designed to convincingly simulate how a human would behave as a conversational partner. Chat bots are typically used in customer service or information acquisition.
Because Bots are getting smarter, their area of use is increasing, even for commercial purposes.
On the other hand, they can also be used for malicious purposes.
♦ The darknet (dark net) 
The darknet is a network, built on top of the normal Internet and it can only be accessed with specific software, like Tor (The onion router).
The darknet allows hiding your identity.
It is a resort for legal and illegal activities.
On the other hand it is the only place to get access to uncensored information in countries where this is not possible.
| Back to start of text |
Back to: Get familiar with the basics of the Internet Back to: Potential dangers on the Internet |

Following, you will find a brief description of vital elements of the Internet.
For easier understanding of this training, a recommended prerequisite is: Get familiar with the basic Internet related terms
|
Back to: Get familiar with the basics of the Internet Back to: Potential dangers on the Internet |
How the Internet has started and the principal structure today
The Internet started in a relatively simple form. In the beginning there were just two computers.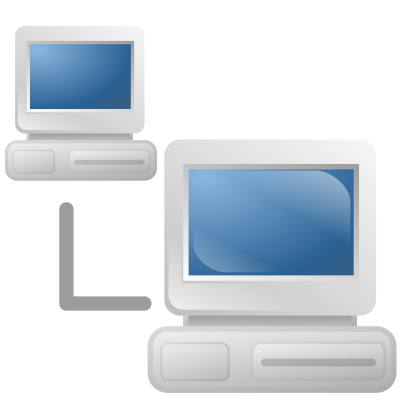 
In 1969, ARPAnet in the USA delivered its first message in a “node-to-node” communication.
Since then, the Internet has grown a lot. In addition, new services have been developed that attracted more and more people.
At present, it is a worldwide collection of big and small networks. 
Because the worldwide web consists of many distributed networks, a message can reach the destination using several ways.
Therefore, the failure of individual networks does not lead to the total collapse of the Internet. The data exchange is then redirected via other networks.
What is an IP address, why it is needed and what does it tell others
A Internet Protocol address (IP address) is a numerical identification assigned to each device connected to a computer  network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. For example, this applies equally to a printer, if it is operated over a network.
network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication. For example, this applies equally to a printer, if it is operated over a network.
Two versions of IP addresses are currently in use:
-
IPv4: 127.77.254.9 or 201.110.109.220
-
IPv6: 2001:db8:0:1234:0:567:8:1
The IPv6 was invented because we are running out of IP addresses in version 4. 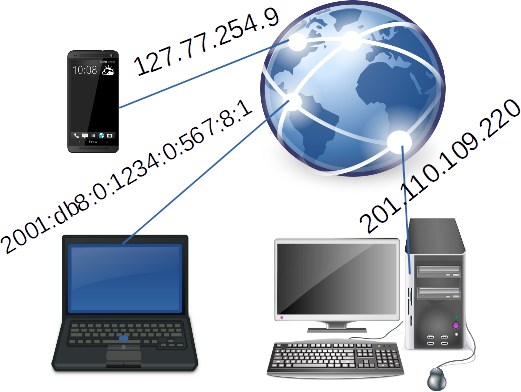
IP addresses are typically provided by Internet service providers (ISP). An IP address fulfils two main functions: device identification and location addressing.
Pairing of IP address to a geographical location is the method used to provide geolocation data. There are times when a content provider wants to identify where the web visitors are located. Sometimes the content is then available only for users at a certain location.
As soon as you visit websites, the following information can be collected: 
- your IP address with your location and service provider (ISP)
- certain details about the used operating system and browser
Converting names of websites into IP addresses (DNS)
Because every device on the Internet is identified by an IP address, it would be extremely embarrassing to enter this long IP address to access a website. That’s why we use names instead.
Fortunately, there is the Domain Name Service (DNS) running in the background, that looks for the corresponding IP address  for a given name. This service works in principle the same way than the old phone book or the contact app on the smartphone.
for a given name. This service works in principle the same way than the old phone book or the contact app on the smartphone.
To speed up the service, parts of the domain name data is locally stored on your device.
By default, the Domain Name Service comes with your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
The DNS is crucial to get the right web sites. A few vendors offer a more secure DNS where malicious sites or websites with inappropriate content are automatically blocked.
Purpose of the device for accessing the Internet at our home
The router at our home opens the door to the Internet. 
Usually, the router is provided by the Internet service provider.
Key functions of the router 
With this, you have your own small network at your home.
A few notes what to consider when opening a website
For accessing a web page, we enter a known name in the browser, like espoo.fi or http://www.espoo.fi. In any case, the browser will automatically add http. 
HTTP stands for "Hyper Text Transfer Protocol". It is a standard protocol used to transmit data over the Internet.
To connect to a server, the web address entered is converted to the corresponding IP address via DNS.
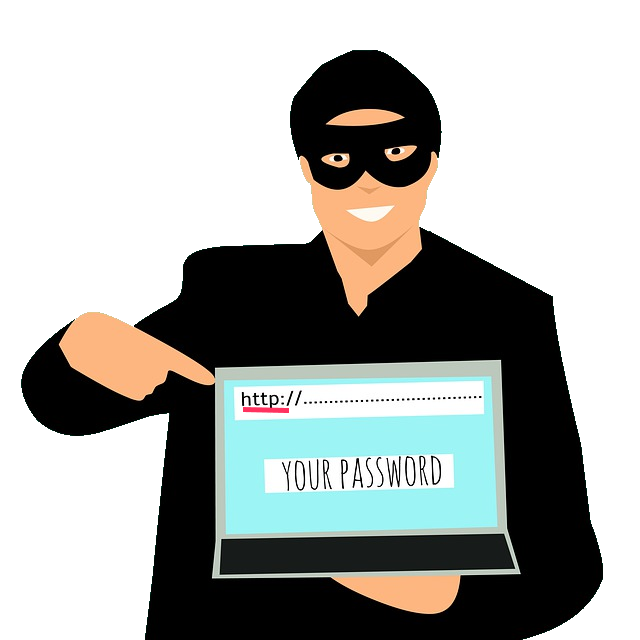 Unluckily, this protocol is not secured. Hackers may read or manipulate the content during transfer over the Internet.
Unluckily, this protocol is not secured. Hackers may read or manipulate the content during transfer over the Internet.
Therefore, HTTPS (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol Secure) is presently used more and more. With HTTPS the data is transmitted encrypted. 
How to see if the data transfer on a website is secured
When ever using web pages where sensitive information needs to be entered, like at online banking, make sure the HTTPS protocol is utilized.
You can see if the data transfer of the website is secured. Check if there is a lock symbol at the beginning of the website’s address in the address bar of the browser. ![]()
By clicking on the lock icon, more information is shown.
| Back to start of text |
Back to: Get familiar with the basics of the Internet Back to: Potential dangers on the Internet |